Complete ecotouristic information database on national parks of Papua (Indonesia).
Papua is the largest and easternmost province of Indonesia. It lies in West Papua region, which comprises the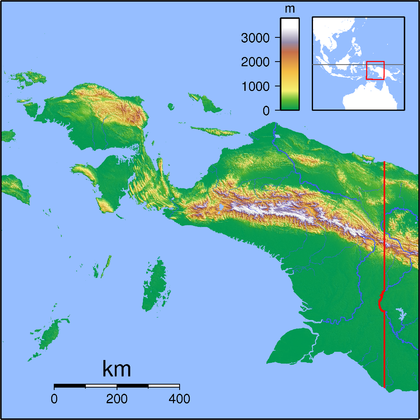 Indonesian, western, half of the island of New Guinea and nearby islands. Papua is bordered by the nation of Papua New Guinea to the east. The population of approximately 3.6 million.
Indonesian, western, half of the island of New Guinea and nearby islands. Papua is bordered by the nation of Papua New Guinea to the east. The population of approximately 3.6 million.
The region is predominantly dense forest where numerous traditional tribes live, although the majority of the population live in or near coastal areas.
The region is 1,200 km from east to west and 736 km from north to south. It has an area of 420,540 km2, which equates to approximately 22% of Indonesia's land area. The border with Papua New Guinea mostly follows the 141st meridian east, with one section defined by the Fly River.
The island of New Guinea was once part of the Australian landmass. The collision between the Indo-Australian Plate and Pacific Plate resulting in the Maoke Mountains run through the centre of the region and are 600 km long and 100 km across. The range includes about ten peaks over 4,000 metres. The tree line is around 4,000 m. Both north and west of the central ranges the land remains mountainous — mostly 1,000 to 2,000 m high with a warm humid climate year round. The highland areas feature alpine grasslands, jagged bare peaks, montane forests, rainforests, fast flowing rivers, and gorges. Swamps and low-lying alluvial plains of fertile soil dominate the southeastern section. Swamps also extend 300 km around the Asmat region.
The province has 40 major rivers, 12 lakes, and 40 islands.The Mamberamo river is the province's largest and runs through the north of the province.
Detailed information on Papua (Indonesia) national parks.
There is a database of Papua national parks available. If you have any question or request you can send it by attached Informative Form.