Basic ecotouristic information on Ngorongoro Conservation Area (Tanzania) - localization, access, characteristic, fauna and flora, possible activities.
Localization
Norhteast Tanzania, 180 km west of Arusha
Access
Easy. The drive from Arusha is around 4 hours along the good road.
Characteristic
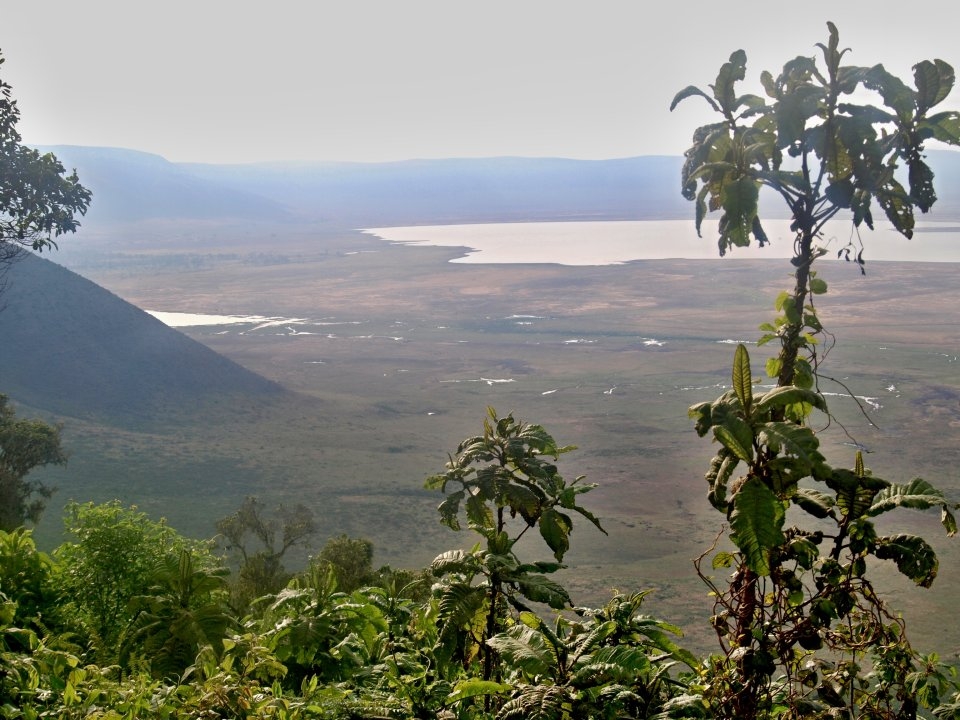
8 288 km2; Altitude 1500 - 3648 m. Worldwide largest inactive, intact, and unfilled volcanic caldera and its surroundings. Caldera is up to 610 m deep and its area is 260 km2. The elevation of the crater floor is 1,800 metres above sea level. A population of approximately 25,000 large animals, largely ungulates. The south and west of the area are volcanic highlands. Further west it continues into plains of Serengeti. The northern and eastern boundaries are approximately defined by the rim of the Great Rift Valley wall, which also prevents animal migration. Typical ecosystems: cloud forest (eastern slopes), grasslands, woodlands, freshwater ecosystems (lakes), wetlands, seasonal salt lake .
Fauna + Flora
Species List - See the Attachment
Possible activities
Animals observation, safari drives
Note
Many archaeological and palaeontological finding places (Oldupai Gorge, Laetoli, Lake Ndutu)
Land in the conservation area is multi-use and unique because it is the only conservation area in Tanzania that protects wildlife while allowing human habitation.
Reserve is listed in World Nature Heritage List of UNESCO from 1979. Ngorongoro area originally was a part of the Serengeti National Park until 1959.
Best time to visit: all the year round.
